Researchers 3D Print Composites with Thermoset Matrix
Carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites are great. As long as they are made with continuous fibers.
When you start chopping these carbon fibers up and mixing them with a thermoplastic base, most of the benefits of a CFRP structure are lost. In the case of chopped fiber filament, the fiber is no longer carrying the load..the weaker polymer matrix is. The carbon fiber is effectively just filler.
So any new method of 3D printing with continuous carbon fibers is of interest to us. If you’re going to print with carbon fiber, may as well reap all the benefits – not just the finish.
This new method devised by a research team at the University of Delaware has demonstrated a method for using a thermoset polymer matrix for their 3D printed composites, as opposed to previous composite printers which have generally used thermoplastic polymer as a matrix.
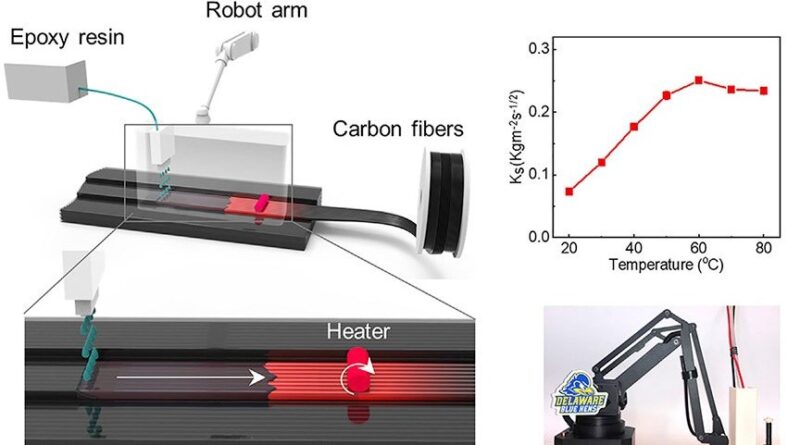
The research team from the Center for Composite Materials (CCM) at University of Delaware recognizes this need for thermoset CFRP printing, and so has developed their Localized In-plane Thermal Assisted 3D printing system (a.k.a “LITA”). It uses a unique printing head and automated robot arm. With this system the team is able to guide the fibers into the required shape, and guide the flow of the liquid polymer by manipulating the temperature of the fibers with a Joule heater. This allows the thermoset resin to flow and wick into the channels between the fibers, before curing to create strong, thermally stable 3D structures.
“The underlying concept of the LITA technique is based on a continuous capillary effect or wicking,which is enabled by a moving thermal gradient along the carbon fiber surfaces, to facilitate the flow of liquid polymer into the tube-like space between neighboring carbon fibers followed by curing of the polymer resin from the heated fiber surfaces to the surrounding space.”
Traditionally fabricated CFRP composites require many hours of post curing. The controlled rapid-curing of the LITA system does not, and therefore there are huge energy savings made by use of this system.
In addition, traditional CFRP is thus-far limited in terms of the geometries allowed by the process. This process, if developed further, may find usage in aerospace, automotive, sports goods, or any other industry that requires light, stiff, fatigue-resistant components that won’t melt during operations.
Source:https://3dprinting.com