
Tech for Sustainable Living
Invent smart waste systems, AI water savers and green energy solutions to power a cleaner world.
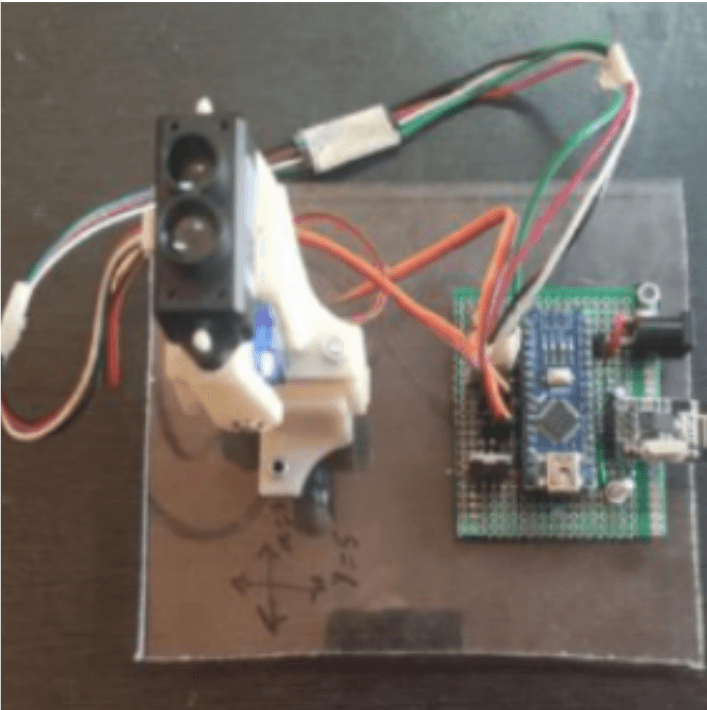
A Computational Approach To Learning Music
Learning the guitar is not an easy task, several people have tried methods like online lessons and even physical ones, yet progress is slow. Due to the above, most quit whilst others find marginal levels of success. Research has been conducted to design a different approach to learning and practicing the guitar. Its purpose is to establish a system in which a user can create music without having to explore the intricacies of music theory, making the task easier and thus more achievable for the general population. By doing so, it strives to make music a more approachable domain for those who wish to explore it. In the process, I devised a unique way of approaching the instrument; one that avoids theory and draws focus on musical sense. Using open CV and python, I designed a program that takes scales as inputs and provides a harmonious sequence of notes as an output. Although based on the guitar, the theory explored in the project can be applied to any fretted instrument that holds a discrete set of notes. Using this program, general users can have access to instruments and consequently the benefits associated with playing music.

A Computational Approach To Learning Music
Learning the guitar is not an easy task, several people have tried methods like online lessons and even physical ones, yet progress is slow. Due to the above, most quit whilst others find marginal levels of success. Research has been conducted to design a different approach to learning and practicing the guitar. Its purpose is to establish a system in which a user can create music without having to explore the intricacies of music theory, making the task easier and thus more achievable for the general population. By doing so, it strives to make music a more approachable domain for those who wish to explore it. In the process, I devised a unique way of approaching the instrument; one that avoids theory and draws focus on musical sense. Using open CV and python, I designed a program that takes scales as inputs and provides a harmonious sequence of notes as an output. Although based on the guitar, the theory explored in the project can be applied to any fretted instrument that holds a discrete set of notes. Using this program, general users can have access to instruments and consequently the benefits associated with playing music.

Quantification of Microplastic in Domestic Greywater Using Image Processing and Machine Learning at Microscopic Level
The abstract discusses the issue of microplastics released from washing synthetic textiles, which contribute significantly to ocean pollution. It highlights the need for innovative methods to detect microplastics in wastewater. The aim of the project is to create a prototype for real-time monitoring of microplastics in greywater released from household washing machines. The prototype includes monitoring using a camera, analyzing and storing data in the cloud, and employing computer vision and machine learning techniques for microplastic detection in the images. It also includes a system for logging and monitoring microplastics in greywater. The prototype can be used by the government to regulate the amount and type of microplastics released by various types of clothes.

Quantification of Microplastic in Domestic Greywater Using Image Processing and Machine Learning at Microscopic Level
The abstract discusses the issue of microplastics released from washing synthetic textiles, which contribute significantly to ocean pollution. It highlights the need for innovative methods to detect microplastics in wastewater. The aim of the project is to create a prototype for real-time monitoring of microplastics in greywater released from household washing machines. The prototype includes monitoring using a camera, analyzing and storing data in the cloud, and employing computer vision and machine learning techniques for microplastic detection in the images. It also includes a system for logging and monitoring microplastics in greywater. The prototype can be used by the government to regulate the amount and type of microplastics released by various types of clothes.

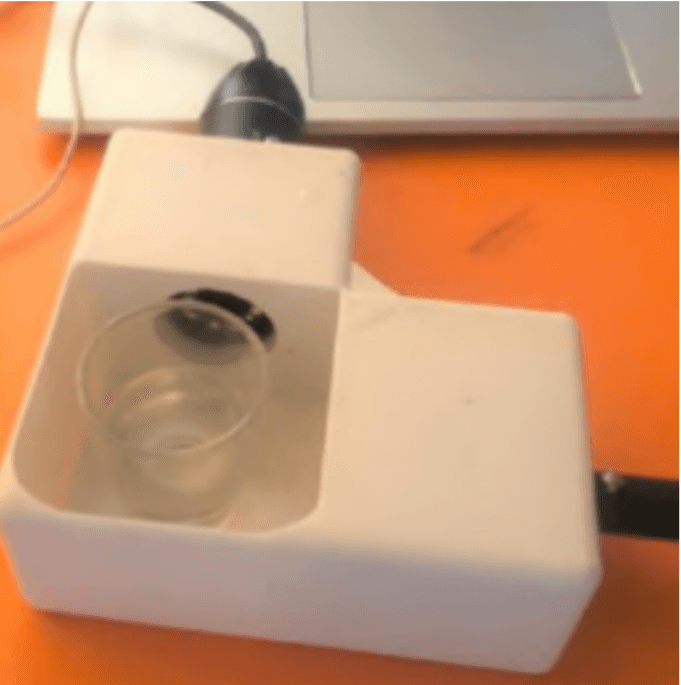
Smart Colourimetric Water Quality Monitoring System Using Test Strips and AI-Enabled Sensor
This project presents an automated colourimetric water-testing system designed to provide low-cost, reliable water quality assessment. A rack-and-pinion strip handler powered by an MG-90 servo and a TCS34725 colour sensor captures calibrated RGB/HSV values, which are processed through a Random Forest Regressor trained on certified laboratory samples. Field tests across Mumbai produced 1,300+ data points, achieving an average error of ±3.7%, a 60% improvement over manual strip readings. The system is affordable (INR 1,500 per device; INR 5 per strip) and includes a behavioural-economic adoption model encouraging community-driven water-quality reporting. The solution enables scalable, accurate, and accessible water monitoring for underserved communities.

Smart Colourimetric Water Quality Monitoring System Using Test Strips and AI-Enabled Sensor
This project presents an automated colourimetric water-testing system designed to provide low-cost, reliable water quality assessment. A rack-and-pinion strip handler powered by an MG-90 servo and a TCS34725 colour sensor captures calibrated RGB/HSV values, which are processed through a Random Forest Regressor trained on certified laboratory samples. Field tests across Mumbai produced 1,300+ data points, achieving an average error of ±3.7%, a 60% improvement over manual strip readings. The system is affordable (INR 1,500 per device; INR 5 per strip) and includes a behavioural-economic adoption model encouraging community-driven water-quality reporting. The solution enables scalable, accurate, and accessible water monitoring for underserved communities.
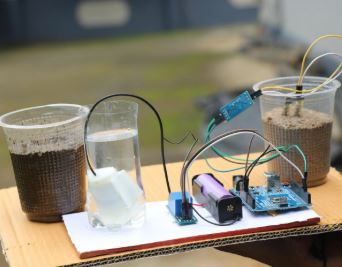
Automatic Water Conservation System
This project presents an IoT-enabled variable-orifice system that regulates water flow in real time to reduce wastage. A flow sensor measures usage patterns and adjusts aperture size automatically, with data logged to the cloud for analysis. The prototype was tested in public washrooms and homes for tasks like handwashing and dishwashing. Results showed significant reductions in water consumption—for example, handwashing usage decreased from 10 L to 7 L in Mode 1 and 5 L in Mode 2. The system demonstrates a practical, data-driven approach to improving household and community water conservation.

Automatic Water Conservation System
This project presents an IoT-enabled variable-orifice system that regulates water flow in real time to reduce wastage. A flow sensor measures usage patterns and adjusts aperture size automatically, with data logged to the cloud for analysis. The prototype was tested in public washrooms and homes for tasks like handwashing and dishwashing. Results showed significant reductions in water consumption—for example, handwashing usage decreased from 10 L to 7 L in Mode 1 and 5 L in Mode 2. The system demonstrates a practical, data-driven approach to improving household and community water conservation.
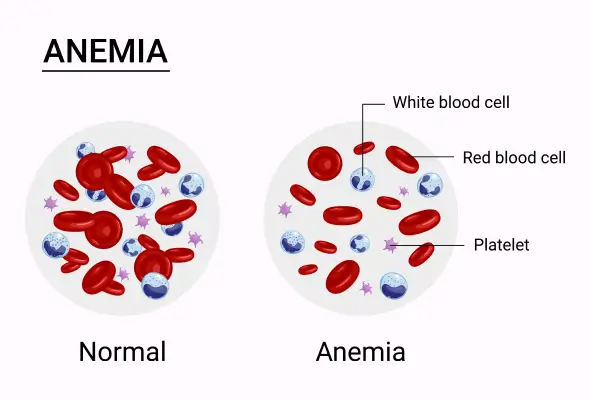
Novel Approach to Detect Anaemia UsingComputer Vision and Machine Learning
While conducting workshops on menstrual health for economically disadvantaged girls in municipal schools, I observed common signs of iron deficiency anaemia, including dark circles under their eyes, stunted growth, frailty, pale palms, and persistent fatigue. Many were unaware of anaemia. Early detection is crucial, especially among children and women, to prevent health issues and ensure proper development. Traditional blood tests are impractical in resource-limited settings like India. To address this, Growth Gauge utilizes smartphone technology and machine learning to predict anaemia probability based on eye images. This cost-effective and accessible solution can support large-scale health programs, enhancing their effectiveness in combating anaemia.

Novel Approach to Detect Anaemia UsingComputer Vision and Machine Learning
While conducting workshops on menstrual health for economically disadvantaged girls in municipal schools, I observed common signs of iron deficiency anaemia, including dark circles under their eyes, stunted growth, frailty, pale palms, and persistent fatigue. Many were unaware of anaemia. Early detection is crucial, especially among children and women, to prevent health issues and ensure proper development. Traditional blood tests are impractical in resource-limited settings like India. To address this, Growth Gauge utilizes smartphone technology and machine learning to predict anaemia probability based on eye images. This cost-effective and accessible solution can support large-scale health programs, enhancing their effectiveness in combating anaemia.
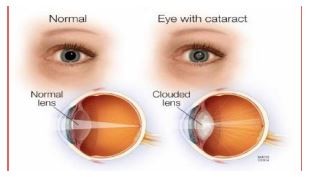
An Autonomous way to detect and quantify Cataracts using Computer Vision
The project focuses on detecting cataracts using Python, aiming to address limitations in current detection methods. Cataracts, a leading cause of blindness in older individuals, pose challenges for diagnosis, especially in rural areas with limited access to ophthalmologists. To overcome these challenges, we developed a program using Python libraries such as OpenCV, NumPy, and FPDF. This program analyzes patient information and eye images to generate a PDF report indicating the presence and severity of cataracts. By creating color masks and incorporating range checks, our program accurately detects cataracts and provides essential information for quantifying the severity of the condition. This solution facilitates early detection and intervention by providing doctors with comprehensive reports for efficient diagnosis.

An Autonomous way to detect and quantify Cataracts using Computer Vision
The project focuses on detecting cataracts using Python, aiming to address limitations in current detection methods. Cataracts, a leading cause of blindness in older individuals, pose challenges for diagnosis, especially in rural areas with limited access to ophthalmologists. To overcome these challenges, we developed a program using Python libraries such as OpenCV, NumPy, and FPDF. This program analyzes patient information and eye images to generate a PDF report indicating the presence and severity of cataracts. By creating color masks and incorporating range checks, our program accurately detects cataracts and provides essential information for quantifying the severity of the condition. This solution facilitates early detection and intervention by providing doctors with comprehensive reports for efficient diagnosis.
The Future of LiFi Technology to Transfer the Data
A Li-Fi network is a novel wireless technology that provides connection within a network. Li-Fi is an abbreviation for light-fidelity, which was proposed by German physicist Herald Haas. It transmits data via illumination by delivering data through an LED light bulb whose intensity fluctuates quicker than the human eye can follow. Practically LiFi is interference-free and safer than radio technology such as Wi-Fi or cellular networks. It involves the use of light instead of radio frequencies to transmit data. Radio frequency communication requires complex radio circuitry, antennas, and receivers, while LiFi is much simpler and uses direct modulation techniques.

The Future of LiFi Technology to Transfer the Data
A Li-Fi network is a novel wireless technology that provides connection within a network. Li-Fi is an abbreviation for light-fidelity, which was proposed by German physicist Herald Haas. It transmits data via illumination by delivering data through an LED light bulb whose intensity fluctuates quicker than the human eye can follow. Practically LiFi is interference-free and safer than radio technology such as Wi-Fi or cellular networks. It involves the use of light instead of radio frequencies to transmit data. Radio frequency communication requires complex radio circuitry, antennas, and receivers, while LiFi is much simpler and uses direct modulation techniques.
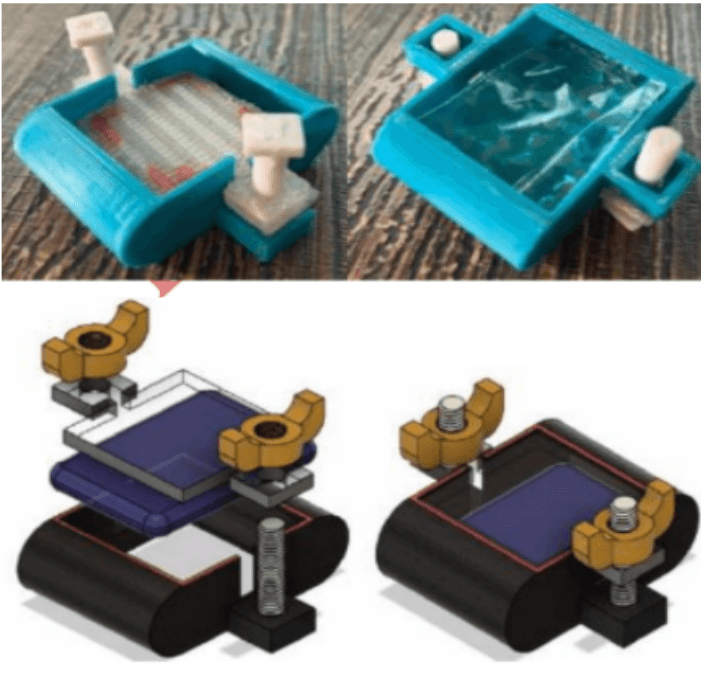
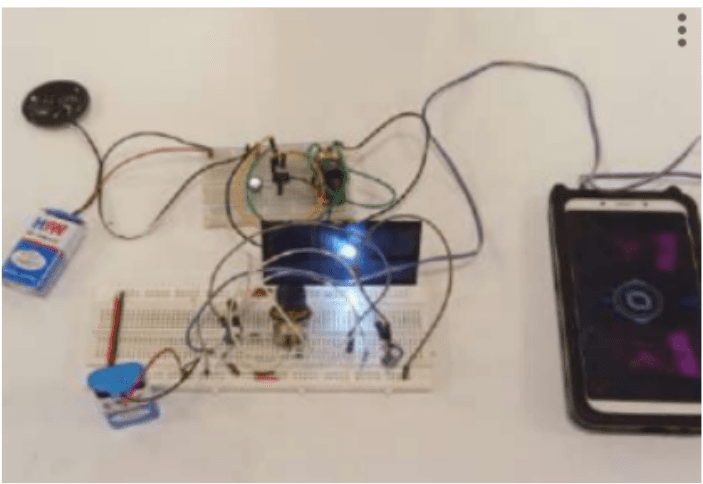
Creating a Haptic 4D Model Along With Machine Learning Analysis by Developing a Non- Invasive Pressure Mapping Method to Screen for Genital Skin Cancer
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.

Creating a Haptic 4D Model Along With Machine Learning Analysis by Developing a Non- Invasive Pressure Mapping Method to Screen for Genital Skin Cancer
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.
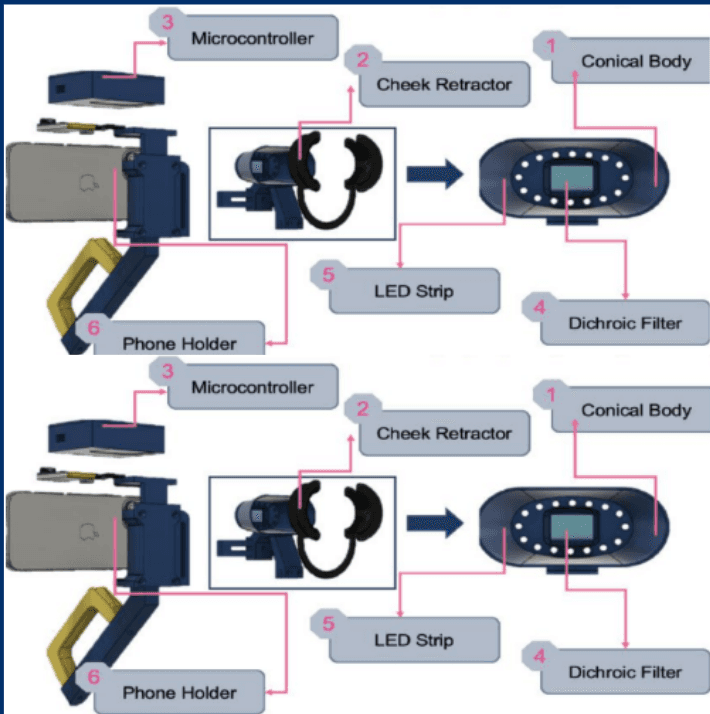
Mouthscope: Autonomous Detection of Oral Precancerous Lesions By Fluorescent Imaging
Oral cancer (OC), highly treatable in early stages, is often diagnosed late in rural India due to lack of accessible screening. MouthScope uses AI to automate OC screening, making it more accessible. It scans the oral cavity for potentially cancerous lesions without professional intervention. The portable device works on auto-fluorescence principle, capturing color differences with a phone camera, which are analyzed by machine learning models (ResNet_v2 and YOLOv5) with 96% accuracy. It allows real-time self-detection and mass screening, enabling self-checkups. Tested on 24 patients, MouthScope clearly distinguished malignant from normal tissue. By using smartphones and machine learning, MouthScope eliminates the need for extensive infrastructure, making mass OC screening more attainable for rural India.

Mouthscope: Autonomous Detection of Oral Precancerous Lesions By Fluorescent Imaging
Oral cancer (OC), highly treatable in early stages, is often diagnosed late in rural India due to lack of accessible screening. MouthScope uses AI to automate OC screening, making it more accessible. It scans the oral cavity for potentially cancerous lesions without professional intervention. The portable device works on auto-fluorescence principle, capturing color differences with a phone camera, which are analyzed by machine learning models (ResNet_v2 and YOLOv5) with 96% accuracy. It allows real-time self-detection and mass screening, enabling self-checkups. Tested on 24 patients, MouthScope clearly distinguished malignant from normal tissue. By using smartphones and machine learning, MouthScope eliminates the need for extensive infrastructure, making mass OC screening more attainable for rural India.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.