
Medical Tech & Wearable Devices
Invent next-gen wearables, AI diagnostic tools, and prosthetics that redefine human health and ability.

Smart Adaptive Machine Learning Based Laptop Stand (Workbit)
White-collar workers and delivery drivers face different health risks due to their work environments. Office workers often experience issues like poor posture and muscle strain from prolonged sitting at computer terminals. To address this, we propose an intelligent stand called "WorkBit" designed to promote work health by monitoring daily habits and providing preventive measures. The stand, mounted on wheels, adjusts its position based on the user's distance from the laptop, promoting better posture and reducing strain on the eyes and neck.

Smart Adaptive Machine Learning Based Laptop Stand (Workbit)
White-collar workers and delivery drivers face different health risks due to their work environments. Office workers often experience issues like poor posture and muscle strain from prolonged sitting at computer terminals. To address this, we propose an intelligent stand called "WorkBit" designed to promote work health by monitoring daily habits and providing preventive measures. The stand, mounted on wheels, adjusts its position based on the user's distance from the laptop, promoting better posture and reducing strain on the eyes and neck.
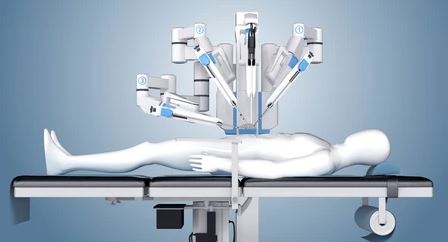
A Review on RoboticsA Review on Robotics Used in Biomedical Surgery
In terms of advancing surgical techniques, robotic surgery, which has been around for more than 20 years is a revolutionary development. The last ten years have seen a rise in the usage of robotics in medical treatments. In an effort to develop smaller, more effective, and less expensive equipment, researchers are ready to achieve record heights as robotic surgery becomes more and more common. Robotic surgery has been successfully used in many hospitals throughout the world and is gaining recognition on a global scale. In this article, we examine robotic surgery's development and progression, current robotic systems, limitations as well as current statistics, and current roles of robotics in surgery, and finally, we discuss the possible roles of robotic surgery in the future.

A Review on RoboticsA Review on Robotics Used in Biomedical Surgery
In terms of advancing surgical techniques, robotic surgery, which has been around for more than 20 years is a revolutionary development. The last ten years have seen a rise in the usage of robotics in medical treatments. In an effort to develop smaller, more effective, and less expensive equipment, researchers are ready to achieve record heights as robotic surgery becomes more and more common. Robotic surgery has been successfully used in many hospitals throughout the world and is gaining recognition on a global scale. In this article, we examine robotic surgery's development and progression, current robotic systems, limitations as well as current statistics, and current roles of robotics in surgery, and finally, we discuss the possible roles of robotic surgery in the future.
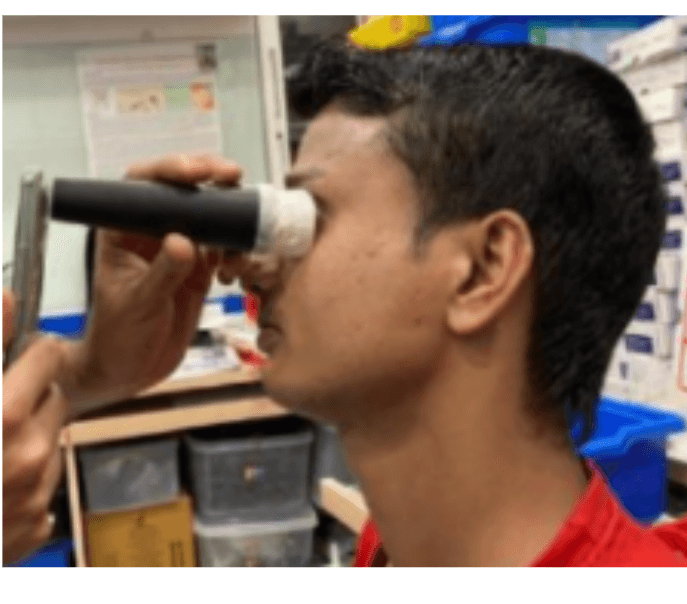
An Autonomous way to detect and quantify
Cataracts using Computer Vision
The project focuses on detecting cataracts using Python, aiming to address limitations in current detection methods. Cataracts, a leading cause of blindness in older individuals, pose challenges for diagnosis, especially in rural areas with limited access to ophthalmologists. To overcome these challenges, we developed a program using Python libraries such as OpenCV, NumPy, and FPDF. This program analyzes patient information and eye images to generate a PDF report indicating the presence and severity of cataracts. By creating color masks and incorporating range checks, our program accurately detects cataracts and provides essential information for quantifying the severity of the condition. This solution facilitates early detection and intervention by providing doctors with comprehensive reports for efficient diagnosis.

An Autonomous way to detect and quantify Cataracts using Computer Vision
The project focuses on detecting cataracts using Python, aiming to address limitations in current detection methods. Cataracts, a leading cause of blindness in older individuals, pose challenges for diagnosis, especially in rural areas with limited access to ophthalmologists. To overcome these challenges, we developed a program using Python libraries such as OpenCV, NumPy, and FPDF. This program analyzes patient information and eye images to generate a PDF report indicating the presence and severity of cataracts. By creating color masks and incorporating range checks, our program accurately detects cataracts and provides essential information for quantifying the severity of the condition. This solution facilitates early detection and intervention by providing doctors with comprehensive reports for efficient diagnosis.
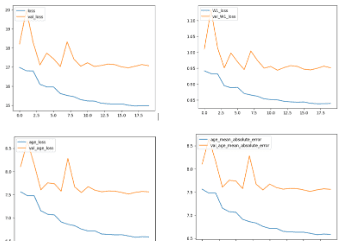
Ocular Age Estimation
A wide range of applications, including biometrics and medical diagnostics, are finding growing value in accurate eye age assessment. This is a thorough examination of the creation of a model for estimating the age of the eye that uses convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to attain a remarkable accuracy rate of 90%. CNNs, known for their skill in image processing, are essential to this approach since they allow for a planned and methodical workflow. Beginning with the collection of a large dataset of eye photographs, the process places an emphasis on the diversity of age groups and eye disorders. It enables businesses to focus their goods and services on certain age groups, improving user experiences, by precisely assessing eye age. The effective integration of CNNs in this model highlights their ability to recognise complex ageing-related patterns, reiterating their status as a strong tool for challenging image-processing tasks.

Ocular Age Estimation
A wide range of applications, including biometrics and medical diagnostics, are finding growing value in accurate eye age assessment. This is a thorough examination of the creation of a model for estimating the age of the eye that uses convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to attain a remarkable accuracy rate of 90%. CNNs, known for their skill in image processing, are essential to this approach since they allow for a planned and methodical workflow. Beginning with the collection of a large dataset of eye photographs, the process places an emphasis on the diversity of age groups and eye disorders. It enables businesses to focus their goods and services on certain age groups, improving user experiences, by precisely assessing eye age. The effective integration of CNNs in this model highlights their ability to recognise complex ageing-related patterns, reiterating their status as a strong tool for challenging image-processing tasks.
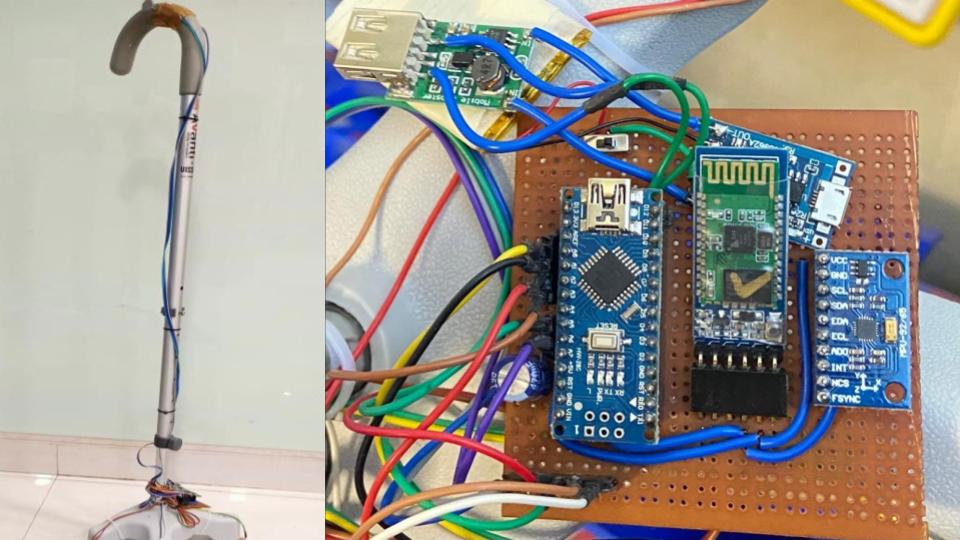
WalkFit
This project presents a smart walking stick designed to improve safety for the elderly by predicting fall risks. The lightweight, user-friendly prototype integrates sensors to monitor tilt angles and pressure distribution in real-time. By collaborating with physiotherapists and leveraging machine learning algorithms, the system analyzes the collected data to anticipate potential falls. This innovative solution provides valuable insights for families and healthcare professionals, demonstrating applications in physiology, neurology, and orthopedics. With its comprehensive approach and adaptability, the smart walking stick offers a promising avenue to enhance the well-being and overall safety of the aging population.

WalkFit
This project presents a smart walking stick designed to improve safety for the elderly by predicting fall risks. The lightweight, user-friendly prototype integrates sensors to monitor tilt angles and pressure distribution in real-time. By collaborating with physiotherapists and leveraging machine learning algorithms, the system analyzes the collected data to anticipate potential falls. This innovative solution provides valuable insights for families and healthcare professionals, demonstrating applications in physiology, neurology, and orthopedics. With its comprehensive approach and adaptability, the smart walking stick offers a promising avenue to enhance the well-being and overall safety of the aging population.
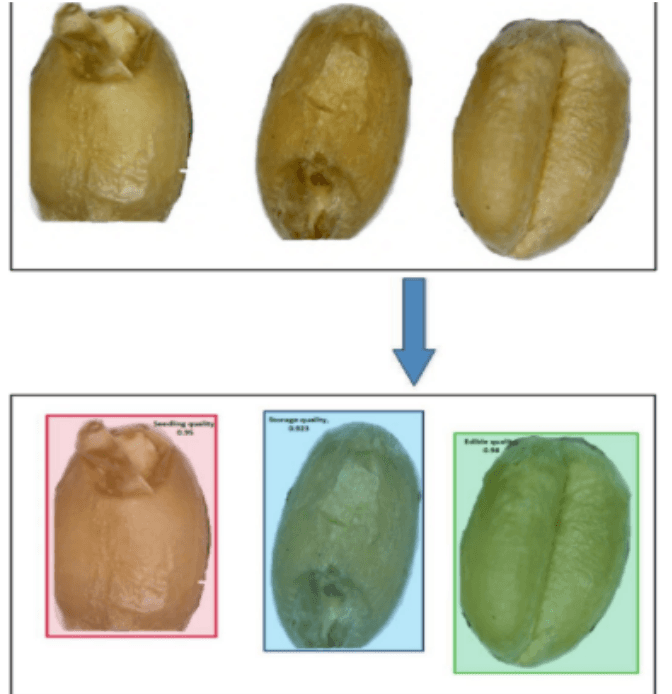
Assessment of Quality of The Wheat Grain Using
Image Processing and Mask R-CNN
The study develops a Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask RCNN) model to classify the quality of wheat grains into four categories: storage quality, edible, seeding quality, or rotten. The model is trained on 122 images created from 2,000 grains, using image processing to extract grain texture. The wheat grains are annotated with VGG Image Annotator, and the JSON files are used for training and testing the Mask RCNN model. The trained model achieves low training and validation losses and demonstrates high accuracy in classifying the grain quality when tested on a new image with all four classes.

Assessment of Quality of The Wheat Grain Using
Image Processing and Mask R-CNN
The study develops a Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask RCNN) model to classify the quality of wheat grains into four categories: storage quality, edible, seeding quality, or rotten. The model is trained on 122 images created from 2,000 grains, using image processing to extract grain texture. The wheat grains are annotated with VGG Image Annotator, and the JSON files are used for training and testing the Mask RCNN model. The trained model achieves low training and validation losses and demonstrates high accuracy in classifying the grain quality when tested on a new image with all four classes.
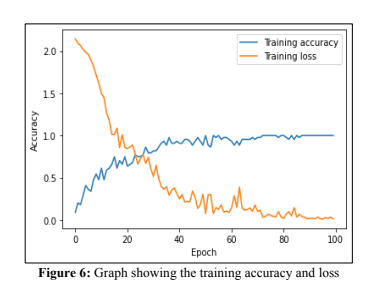
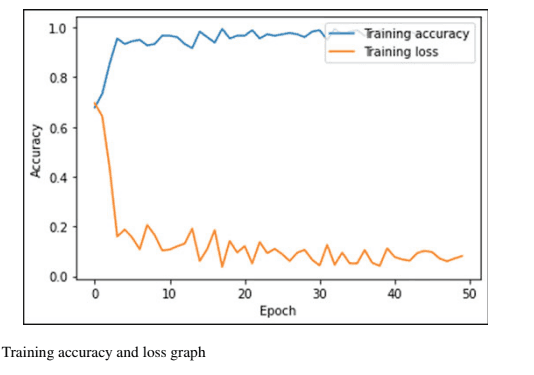
A Model to Identify the Impairment Caused by Smoking to the Oral Cavity
This project addresses the detection and classification of oral mucosal impairments caused by smoking or other factors using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The CNN model is trained and tested on a dataset of 1,788 images categorized into three classes: healthy mucosa, impairments due to smoking, and impairments due to other factors. The dataset is split into 70% for training and 30% for validation. The developed CNN model achieves remarkable training and test accuracies of 99.95% and 100%, respectively, with training and test loss values of 0.0151 and 0.0023. This intelligent system enables accurate detection and differentiation of oral mucosal impairments, providing valuable diagnostic support for healthcare professionals.

A Model to Identify the Impairment Caused by Smoking to the Oral Cavity
This project addresses the detection and classification of oral mucosal impairments caused by smoking or other factors using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The CNN model is trained and tested on a dataset of 1,788 images categorized into three classes: healthy mucosa, impairments due to smoking, and impairments due to other factors. The dataset is split into 70% for training and 30% for validation. The developed CNN model achieves remarkable training and test accuracies of 99.95% and 100%, respectively, with training and test loss values of 0.0151 and 0.0023. This intelligent system enables accurate detection and differentiation of oral mucosal impairments, providing valuable diagnostic support for healthcare professionals.
An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening
Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof

An Artificial Intelligence Integrated Technique for Screening
Neurological Diseases with Sound as a Biomarker
This project aims to develop a machine learning-based system for detecting neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease (PD) and paralysis through voice analysis. Researchers recorded speech samples from patients and healthy individuals, extracting features using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) models were trained on this dataset to classify voices into PD, paralysis, or normal categories. With an overall accuracy rate comparable to human laryngologists (60.1% and 56.1%), this system can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the presence and stage of neurological disorders, enabling appropriate treatment recommendations through therapy, medication, or a combination thereof

Environmental Technology or Environmental Safety
Sewage disposal cleanup is a hazardous job, exposing workers to harmful gases, infections, and health risks like musculoskeletal disorders and respiratory problems. SEWER GUARD is a project aimed at developing an information and communication ecosystem to monitor and alert workers about dangerous gas levels in sewers. It uses MQ series sensors to measure gas levels and sends alerts if they exceed safe thresholds. The system correlates gas intensity, depth, and exposure time, enabling workers to evacuate before conditions become life-threatening. An Android app and cloud storage are integrated for monitoring and data storage. Authorities can also be notified via SMS if sewage overflow is likely. SEWER GUARD aims to improve the safety and working conditions of sanitary workers engaged in sewer cleanup operations.

Environmental Technology or Environmental Safety
Sewage disposal cleanup is a hazardous job, exposing workers to harmful gases, infections, and health risks like musculoskeletal disorders and respiratory problems. SEWER GUARD is a project aimed at developing an information and communication ecosystem to monitor and alert workers about dangerous gas levels in sewers. It uses MQ series sensors to measure gas levels and sends alerts if they exceed safe thresholds. The system correlates gas intensity, depth, and exposure time, enabling workers to evacuate before conditions become life-threatening. An Android app and cloud storage are integrated for monitoring and data storage. Authorities can also be notified via SMS if sewage overflow is likely. SEWER GUARD aims to improve the safety and working conditions of sanitary workers engaged in sewer cleanup operations.

Environmental Technology or Environmental Safety
The research presented here looks into the vibration properties of 3D-printed airless tires, which have the potential to revolutionize tire design and transportation efficiency. Through extensive experimentation and vibration research, three distinct tire constructions were investigated. Because of its good damping and deformation qualities, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) was chosen as the 3D printing material. The experimental arrangement was designed to simulate real-world road conditions, and an MPU6050 sensor captured tire vibrations in three axes. The vibrational properties of the tire structures were revealed using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) analysis, allowing for a comparative assessment of their stability. Structure 1 was found to be the most vibration-stable, followed by Structures 3 and 2.
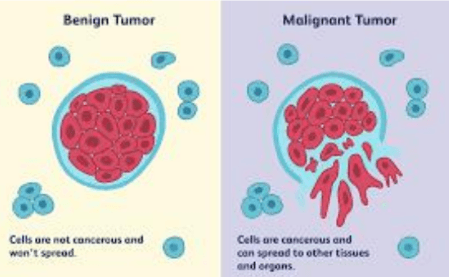
Creating a Haptic 4D Model Along With Machine Learning Analysis by Developing a Non- Invasive Pressure Mapping Method to Screen for Genital Skin Cancer
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.

Creating a Haptic 4D Model Along With Machine Learning Analysis by Developing a Non- Invasive Pressure Mapping Method to Screen for Genital Skin Cancer
Early detection of genital skin cancer is hindered by factors such as privacy concerns, social barriers, and discomfort. Traditional biopsy methods, though accurate, can cause pain and infection in the genital region. Our engineering objective is to develop a non-invasive screening method using machine learning. We created a mobile app that processes lesion images through a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), achieving an 83% accuracy in classifying malignant lesions. Additionally, we employ a pressure mapping kit to create a 3D flexible printing file, providing tactile feedback for accurate diagnosis.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.
Find your nearest innovation lab
These awards reflect projects that pushed my boundaries, told deeper stories, and caught the attention of people who care about what visuals can say.